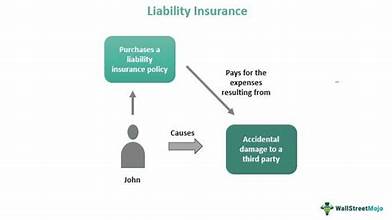
Liability insurance is a vital protection for individuals and businesses, safeguarding against financial losses resulting from legal liability for injuries or damages to others. This essential coverage shields assets from lawsuits, covering medical expenses, property damage, and personal injury claims, such as libel and slander. By having liability insurance, businesses can protect their reputation, maintain customer trust, and comply with regulatory requirements. Moreover, it helps cover legal fees and settlements, ensuring that unexpected events don’t lead to financial ruin. Whether you’re a business owner, professional, or individual, liability insurance provides peace of mind, knowing you’re prepared for the unexpected.
Liability insurance policies include:
- General Liability Insurance
- Professional Liability Insurance (Errors & Omissions)
- Product Liability Insurance
- Directors and Officers Liability Insurance (D&O)
- Cyber Liability Insurance

Types Of Liability Insurance:
1. Professional Liability Insurance:
Professional Liability Insurance, also known as Errors and Omissions (E&O) insurance, protects professionals against claims of negligence, errors, or omissions in their work. It covers damages and legal fees resulting from alleged professional mistakes or failures to deliver services as promised.
Claims Examples for Professional Liability
- For misdiagnosing a patient’s ailment, a doctor faces legal action.
- A lawyer is charged with losing clients because they failed to complete paperwork on time.
- A claim is filed against a financial advisor for suggesting inappropriate investments.
- An architect is charged with creating a structure that has structural defects.
2. General Liability Insurance:
A comprehensive insurance policy designed to protect businesses, organizations, and individuals from financial losses resulting from third-party claims of:
- Bodily injury (physical harm or death)
- Property damage (damage to others’ property)
- Personal injury (libel, slander, defamation, invasion of privacy, etc.)
- Advertising injury (copyright infringement, trade libel, misappropriation, etc.)
- Product liability (damages or injuries caused by products manufactured or sold)
3. Product Liability Insurance:
Product liability insurance protects businesses from financial loss if a product they manufacture, distribute, or sell causes injury or damage to a third party. This insurance is crucial for companies involved in producing or selling physical goods, as it helps cover legal costs, medical expenses, and compensation claims related to product defects, design flaws, improper labeling, or failure to provide adequate warnings.
- Protects your business from costly lawsuits and settlements
- Covers damages and legal fees related to product liability claims
- Helps maintain your business reputation and credibility
- Required by many retailers and distributors as a condition of doing business
4. Personal Liability Insurance:
Personal Liability Insurance protects individuals and their families from financial losses due to claims of injury or damage to others. It provides coverage for damages, legal fees, and medical expenses related to claims of:
- Bodily injury
- Property damage
- Personal injury (libel, slander, etc.)
- Rental property damage (if you rent out a property)
Benefits of Liability Insurance:
Protecting Your Money
- Pays settlements and attorney fees
- Safeguards company resources
Observance
- Complies with regulations
- Steers clear of fines and penalties
Continuity of Business
- Preserves business while legal proceedings
- Upholds credibility
Protection of Reputation
- Exhibits accountability
- Increases trustworthiness
Extra Advantages
- Premiums deducted from taxes
- Enhanced company reputation
- Superior risk mitigation
Key Components of Liability Insurance:
1. Policy Limits:
The policy limit is the maximum amount the insurance company will pay for a claim. Liability insurance typically has two types of limits:
- Per Occurrence Limit: The maximum amount the insurer will pay for a single claim.
- Aggregate Limit: The total amount the insurer will pay during the policy period, regardless of the number of claims.
It’s important to choose a policy with limits that adequately cover potential risks, especially in high-risk industries.
2. Deductibles:
The deductible is the amount the insured must pay out-of-pocket before the insurance coverage kicks in. Higher deductibles often result in lower premiums but can lead to higher costs in the event of a claim.
3. Exclusions:
Exclusions are specific situations or types of claims not covered by the policy. For example, liability insurance may exclude coverage for intentional harm, criminal acts, or contract disputes. Reviewing these exclusions carefully is crucial to ensuring that the policy meets the insured’s needs.
4. Claims-Made vs. Occurrence Policies:
Liability insurance policies can be either “claims-made” or “occurrence” policies:
- Claims-Made Policies: These policies only cover claims made during the policy period. If a claim arises after the policy expires, it will not be covered unless the insured purchases extended coverage (tail coverage).
- Occurrence Policies: These policies cover incidents during the policy period, even if the claim is filed after the policy has expired.
Choosing the right type of policy depends on the nature of the risks involved and the potential for delayed claims.
Factors Affecting Liability Insurance Premiums:
Industry-specific Elements
- Sales volume and revenue
- The number of workers and payroll
- The kind of goods or services provided; 4. The operations and procedures of the business
- Safety documentation and procedures
- Adherence to rules and guidelines
Sector-Specific Elements:
- History of medical malpractice (healthcare)
- Vehicle History (transportation)
- Manufacturing history of product recalls
- Certifications and licenses for professionals (services)
- Environmental hazards related to building and manufacturing
Factors Particular to Insurance:
- The duration of the policy and its renewal history
- The underwriting policies and risk appetite of the insurer
- Fees for brokers or agents
- Premium taxes and surcharges
- Discounts (such as loyalty programs and package policies)
Economic and Regulatory Factors:
- Modifications to laws and rules
- Jury awards and litigation trends
- The state of the economy (interest rates, inflation)
- Supply and demand in the insurance sector
How to Choose a Liability Insurance Policy:
Choosing the best liability insurance coverage requires serious consideration of several issues. Here’s a step-by-step approach to assist you in choosing wisely:
Step 1: Assess your risks:
- Determine the risks and liabilities related to your line of work or business.
- Take into account the seriousness and regularity of possible claims.
- Assess the operations, goods, and services of your company.
Step 2: Determine Policy Needs:
- Decide on the type of liability insurance needed (e.g., general, professional, product).
- Consider policy limits (per occurrence and aggregate) and deductibles.
- Think about additional coverage options (e.g., umbrella, cyber).
Step 3: Research Insurers:
- Seek for insurers who have experience in your sector.
- Verify financial stability ratings (such as Moody’s and A.M. Best).
- Assess the reputation of the insurance for handling claims.
Step 4: Compare Policies:
- Examine the terms, conditions, and exclusions of the policy.
- Examine rates, deductibles, and coverage restrictions.
- Look for savings opportunities (such as loyalty plans and package policies).
Step 5: Evaluate Policy Features:
- The coverage area (local, national, or worldwide).
- Coverage of defense costs (inside or beyond policy limitations).
- Options for settlement (such as lump amount and installment).
- Terms of policy cancelation.
Step 6: Consult With an Expert:
- A broker or agent that specializes in liability insurance.
- Clarify policy details and pose queries.
- Receive recommendations based on your requirements.
Step 7: Review and Update:
- Regularly examine your policy to verify adequacy.
- Modify the policy as your company develops.
- Take into account changing the coverage, deductibles, or limits.
Conclusion:
Liability insurance is a critical component of risk management for individuals and businesses. It protects against the unpredictable costs of lawsuits, settlements, and legal defense, ensuring that the insured can focus on their core activities without fear of financial ruin.
Whether you’re a small business owner, a professional offering specialized services, or a manufacturer of products, having the right liability insurance is essential to protect yourself from the unexpected. With various types of coverage available, assessing your specific risks and choosing a policy that offers adequate protection is important. By doing so, you’ll not only safeguard your financial future but also gain peace of mind knowing that you’re prepared for any legal challenges that may come your way.